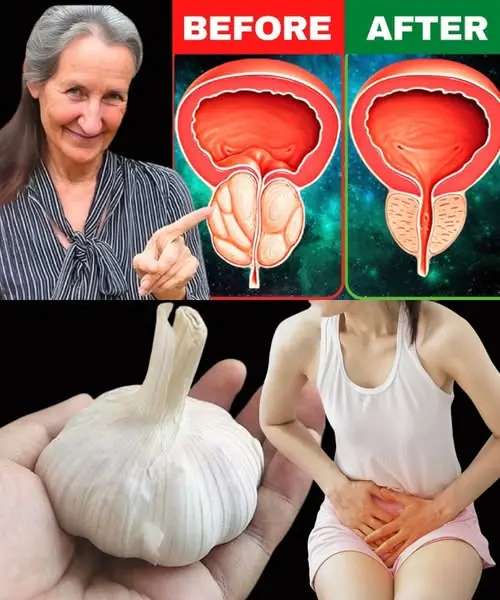
Home Tips 2025-03-17 02:46:56
Excessive Saliva Production in the Mouth
News in the same category

Home Tips 17/03/2025 21:56
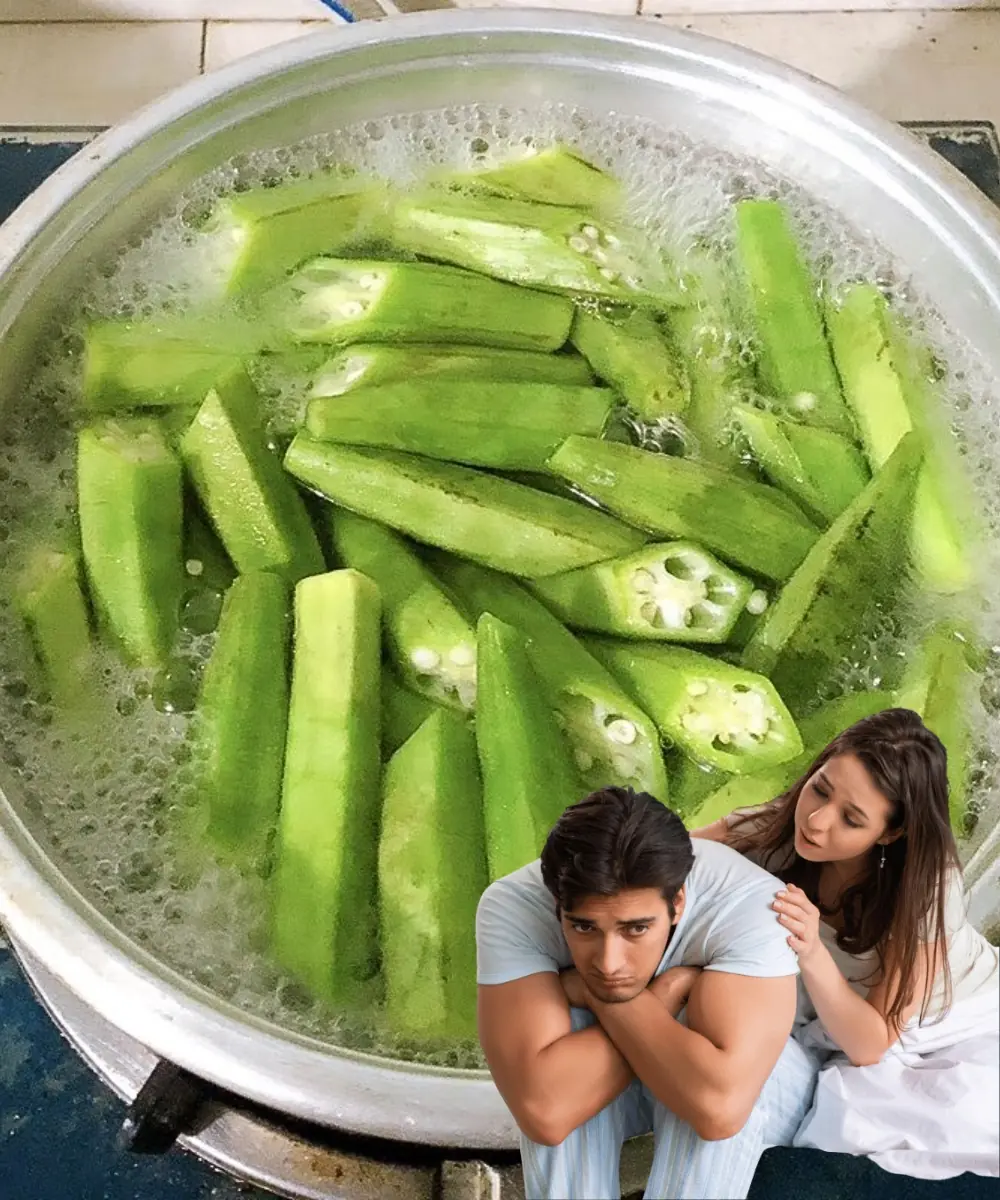

The Secret Power of Okra Water: Why You Should Start Drinking It Today!
Home Tips 17/03/2025 21:55
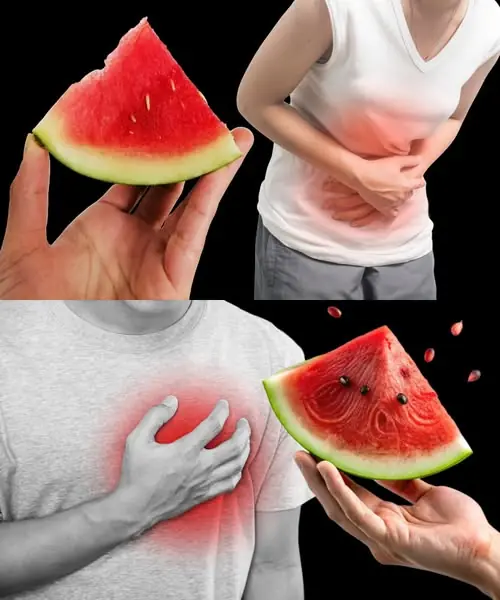
Cleanse Your Intestines, Liver, and Kidneys in Just 3 Days – Naturally!
Home Tips 17/03/2025 21:53
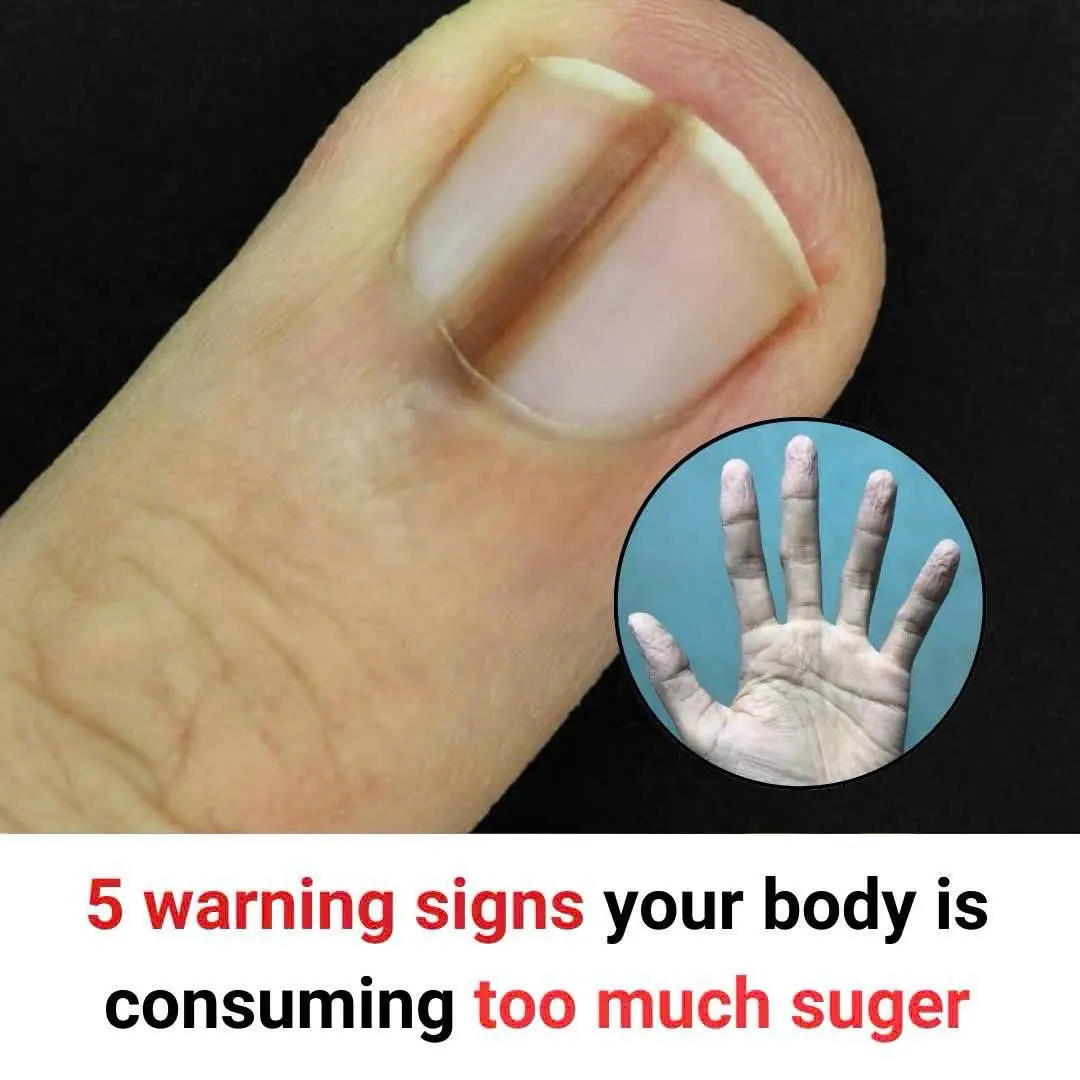
5 warning signs your body is consuming too much suger
Home Tips 17/03/2025 21:46

5 foods rich in estrogen
Home Tips 17/03/2025 02:54

A month before a stroke, your body warns you: 10 signs not to ignore
Home Tips 17/03/2025 02:40
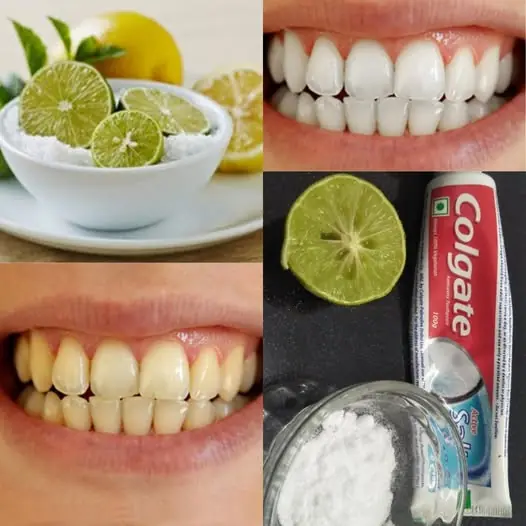

10 Natural Ways to Whiten Teeth at Home
Home Tips 17/03/2025 02:33
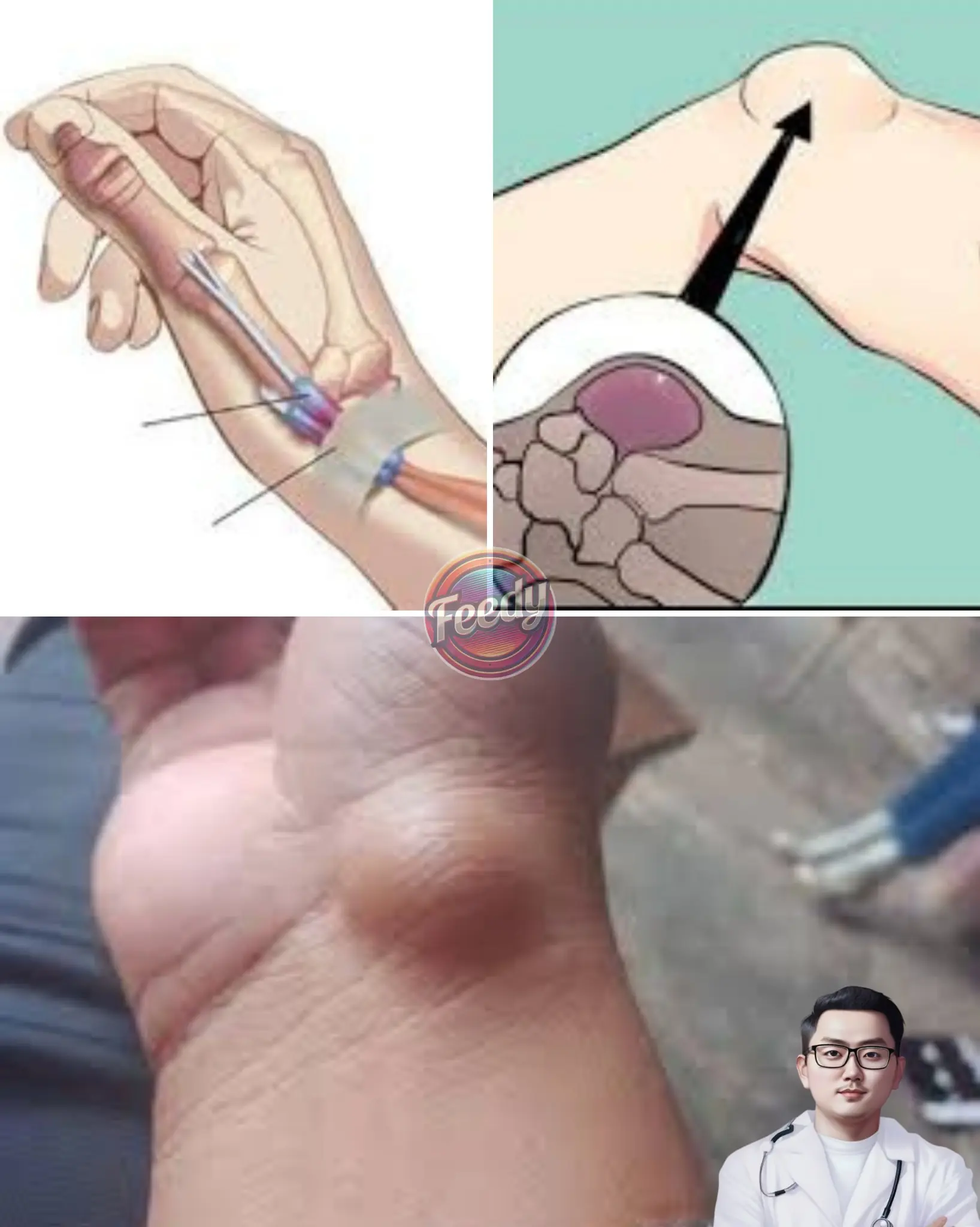
Castor Leaves: Traditional Benefits and Important Precautions
Home Tips 17/03/2025 02:18
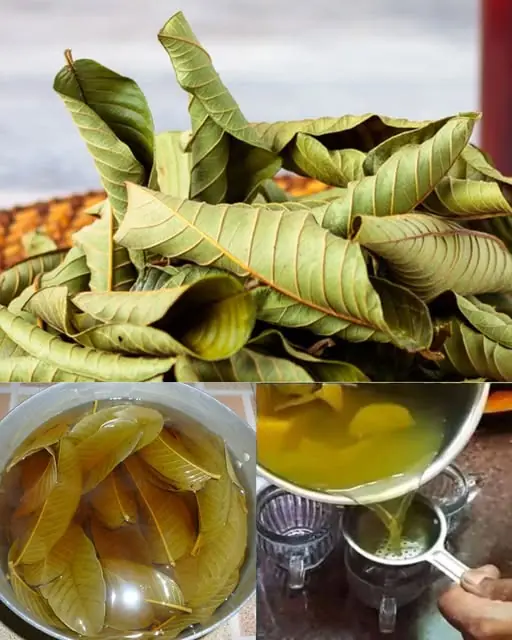

Health Benefits of Guava Leaf Tea: A Natural Remedy for Wellness
Home Tips 16/03/2025 22:18
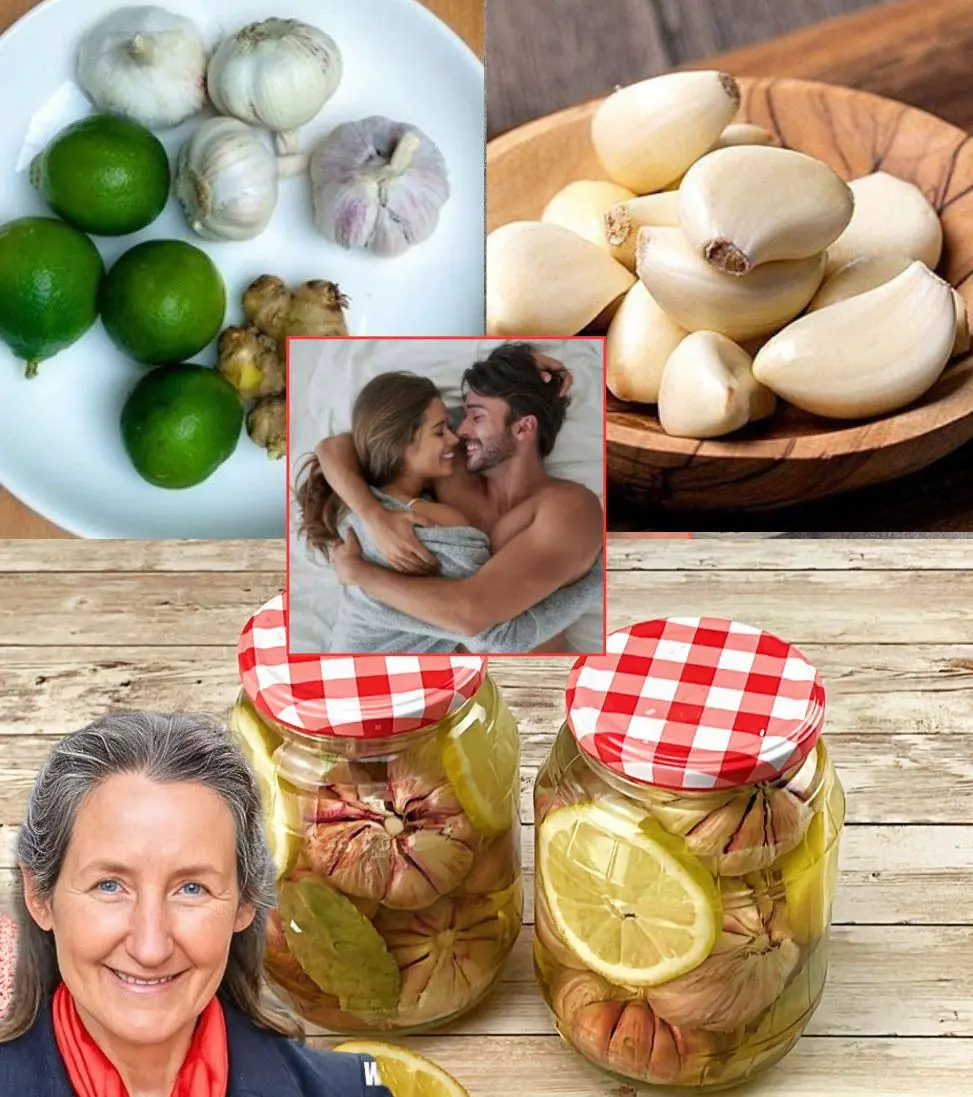

How Garlic and Lemon Can Elevate Your Performance in the Bedroom
Home Tips 16/03/2025 19:31
The Incredible Health Benefits of Dates: Nature’s Sweet Superfood
Home Tips 16/03/2025 10:08
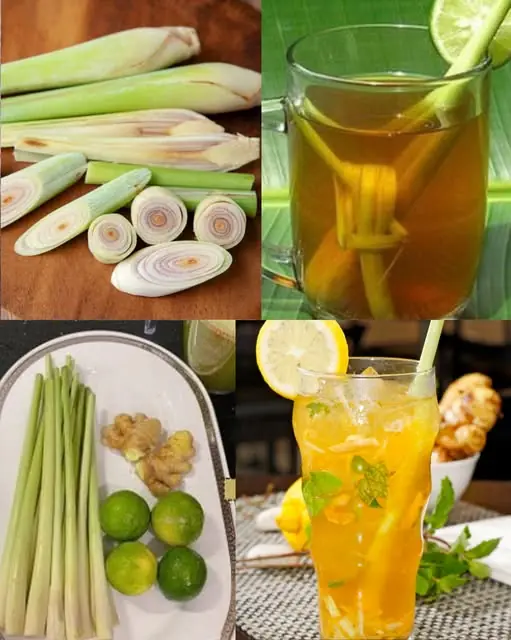

How to Make a Cup of Lemon, Lemongrass, Ginger, and Honey Drink to Detox Your Kidneys, Cleanse Your Liver, and Boost Immunity at Home
Home Tips 16/03/2025 10:06

Waking Up Between 3 and 5 AM Could Be a Sign of Spiritual Awakening
Home Tips 16/03/2025 09:57

I can't even believe it myself
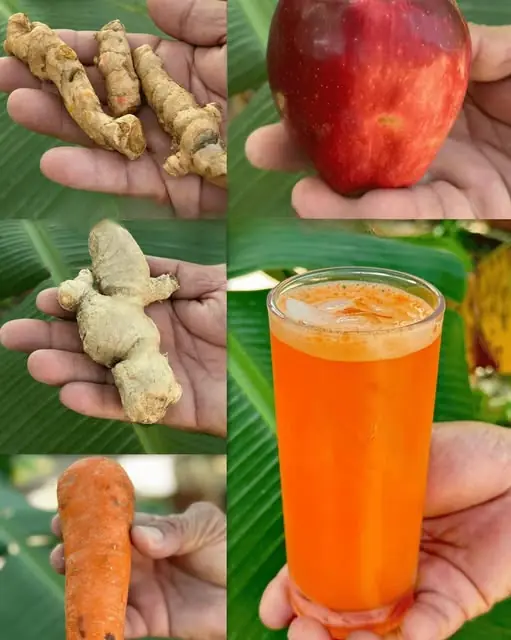

Recommended this smoothie, and one glass a day was sufficient to naturally resolve these problems.
Fatty Liver: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Home Remedies
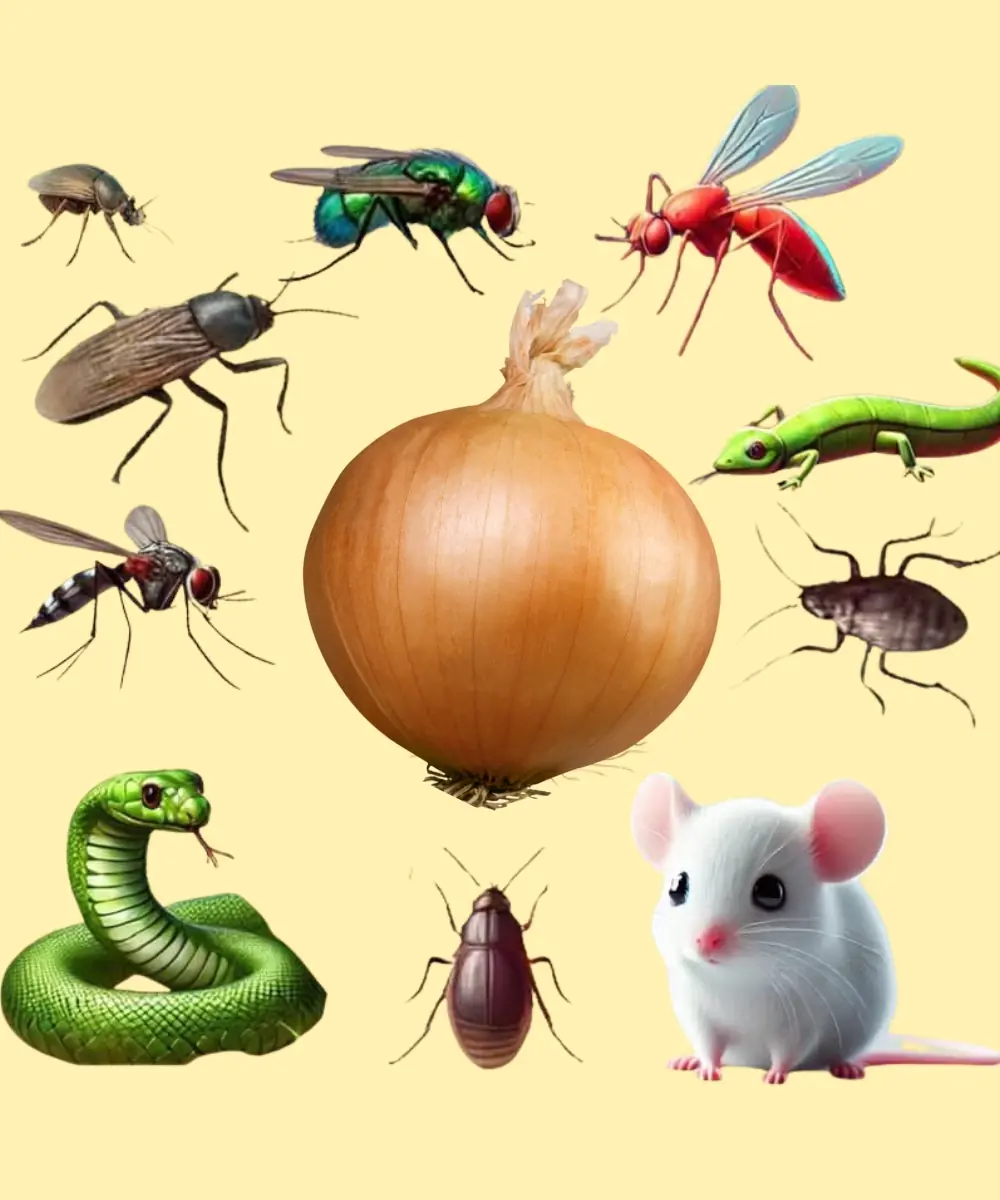

Onions: A Natural Way to Get Rid of Pests

Excessive Saliva Production in the Mouth: A Warning Sign of Health Issues You Shouldn’t Ignore😪👇
News Post

How To Get Peace Lilies To Bloom More Often
Home Garden 20/03/2025 04:21

How To Grow Zucchini In A Pot: An effective 6 steps guide
Home Garden 20/03/2025 04:19

15 Vegetables You Can Harvest in 30 Days
Home Garden 20/03/2025 04:17

The Black Serum To Get Long, Black Hair
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:57

Oil Infusion For Fast Hair Growth
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:54

Turmeric Eye Mask For Dark Circles
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:51

DIY Night Cream To Get Glow And Lovely Skin Naturally
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:48

Rice Flour & Flax Seeds Mask For Instant Glow & Younger Looking Skin
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:43

Tomato To Treat Hyperpigmentation, Dark Spots On Your Face
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:39

Beetroot Gel For Face
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:34

Collagen booster night cream!!
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:24

Homemade Anti-Aging Hand Scrub To Get Younger Looking Hands
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:19

Collagen booster night cream!!
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:14

How to use rice water to get clear & glowing skin naturally
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:11

Miracle Indian Bridal Ubtan For Skin Brightening
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:07

Turmeric Eye Mask For Dark Circles
Beauty 20/03/2025 03:02

DIY Keratin Treatment at Home for Smooth, Frizz-Free Hair
Beauty 20/03/2025 02:59

Collagen Combo For Glass Skkin
Beauty 20/03/2025 02:57

Beauty Cubes For Bright Glowing Skin
Beauty 20/03/2025 02:54

DIY Extremely Hydrating Aloe Vera Night Gel
Beauty 20/03/2025 02:51